
This is sponsored content. Barchart is not endorsing the websites or products set forth below.
Day trading, the practice of buying and selling securities within a single trading day, can be a thrilling yet complex endeavor. It offers the potential for high returns but also comes with significant risk and requires a substantial investment of time, effort, and, most importantly, the capital.
The question "How much money do I need to start day trading?" is one of the most common queries among aspiring traders. The answer, however, is not as straightforward as one might hope. It depends on various factors, including the trader's location, chosen market, trading strategy, risk tolerance, and legal and regulatory conditions.
Whether you're a budding trader curious about the capital required or a seasoned player looking for a deeper understanding, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into the financial dynamics of day trading.
Capital Acquisition: Financing Options to Start Day Trading
The initial capital investment in day trading is a crucial aspect that determines the flexibility and potential profitability of your trading operations. There are several ways aspiring traders can raise this capital, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages. Here, we take an in-depth look at these financing options.
Online Lending Platforms
Online lenders offer various loan products, often with quicker approval times than traditional banks. On COMPACOM, a reliable online comparison site, you can explore multiple options like payday loans and personal loans, even for individuals with poor credit.
Personal Savings
The most direct and least complicated way to fund your day trading venture is to utilize your savings. It allows you the freedom to trade without the pressure of repayment schedules and interest rates. However, it's essential to balance this against the risk of potential losses and the impact on your financial security.
No Credit Check Loans
For those with a low credit score or no credit history, no credit check payday loans present a viable option. These loans offer quick access to capital without a credit check but usually come with high-interest rates and fees. It's crucial to ensure the loan's cost doesn't outweigh its benefit.
Home Equity Loans
If you're a homeowner with substantial equity in your home, a home equity loan can provide a large sum of capital. These loans typically have lower interest rates than personal loans or credit cards, but they carry the risk of foreclosure if you fail to make repayments.
Quick Payday Loans
Online payday loans, accessible via online lending platforms, provide immediate liquidity for short-term needs. However, their convenience is tempered by high costs, so they should be considered a last resort rather than a primary funding strategy.
Retirement Funds
Some may consider tapping into their retirement funds like 401(k) or IRA. While this provides immediate access to capital, the long-term implications can be significant. Premature withdrawals often incur penalties and could jeopardize your retirement security.
Personal Loans for Bad Credit
There are specific lending products designed to cater to individuals with poor credit scores. A common example of such a product is a $5,000 loan for bad credit. This type of loan is particularly useful for those who might face difficulties in securing traditional bank loans due to their credit history.
Raising capital for day trading involves careful consideration of the associated costs and risks. While these financing options can assist in amassing the necessary funds, it's essential to weigh their potential drawbacks. Borrowing money to invest can amplify both gains and losses. It is always advisable to conduct thorough research and consider seeking advice from a financial advisor before making such critical decisions.
What is Day Trading?
Day trading is a specific form of a trading strategy where financial instruments like stocks, currencies, or commodities are bought and sold within the same trading day. The key idea is that all positions are closed before the market closes for that trading day, ensuring that no position is held overnight.
The objective of day trading is to capitalize on small price movements in highly liquid markets, often by making numerous trades each day. Day traders use a variety of strategies, including scalping, range trading, and news-based trading.
It's important to note that day trading requires a significant investment of time. Many day traders treat it like a full-time job, spending several hours each day researching, monitoring markets, and executing trades. The capital requirements can be substantial, especially when considering regulatory constraints such as the Pattern Day Trader rule.
Day trading also carries a high level of risk, as rapid price fluctuations can lead to substantial losses. Consequently, it's not recommended for everyone, and potential day traders should carefully consider their risk tolerance and financial circumstances before diving in.
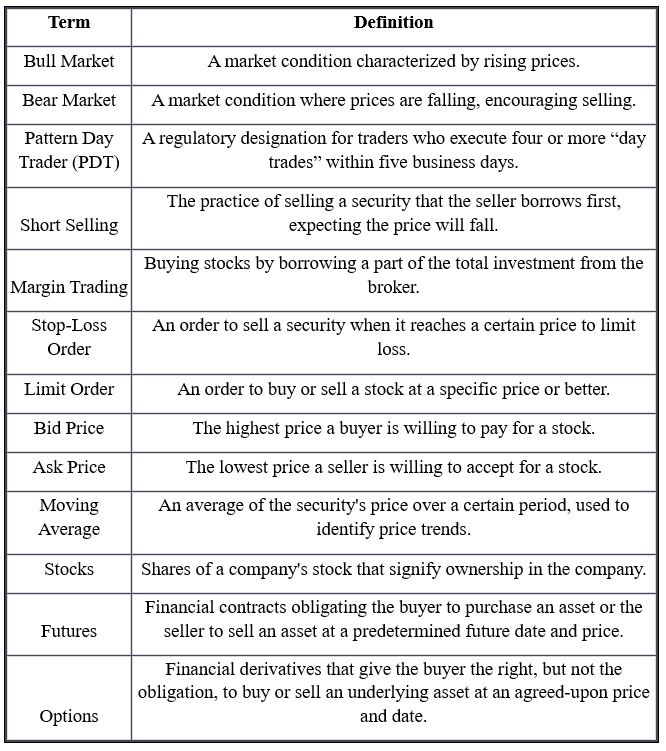
Here's a table listing and defining some common day trading terminologies:
How Much Money Do You Need to Start Day Trading?
Initiating your journey into day trading is contingent upon understanding the financial commitment required. This commitment varies significantly, depending on factors like the market you select, your chosen trading strategy, and individual risk tolerance. Below, we detail these factors and their influence on the capital you'd need to start.
Market Selection
The market you decide to trade in can significantly affect your initial capital requirement. For instance, if you choose to day trade stocks in the U.S., you'll need to meet the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority's (FINRA) minimum account balance requirement of $25,000. However, if you opt for the Forex or futures market, you might be able to start with as little as $1,000.
Trading Strategy
Your chosen trading strategy also plays a pivotal role in determining your capital requirement. Scalping, a strategy involving making many trades for small profits, might be viable with an account balance as low as $2,000 to $5,000. In contrast, more capital-intensive strategies, like swing trading, could require over $10,000.
Regulatory Requirements
Legal requirements can also dictate your starting capital. As per the U.S.' Pattern Day Trader rule, day traders need to maintain a minimum equity of $25,000 on any day that they trade.
Risk Tolerance
How much risk you're willing to take on will also determine your initial capital. If you're risk-averse and wish to limit potential losses to no more than 1% of your trading capital on any single trade, you would need a larger account balance. For example, if you're not willing to lose more than $200 per trade, you would need a starting balance of at least $20,000.
Lifestyle Requirements
If day trading is intended to be your primary income source, your starting capital should be substantially higher. Experts often recommend starting with at least $30,000 to $50,000 to generate enough profits after covering your living expenses and trading costs.
In the following chart, we present a comparison of the average capital required for day trading in different markets, including Forex, Stocks, Futures, Options, and Cryptocurrency.
In conclusion, the amount of capital required to start day trading depends on a multitude of factors and varies greatly from one trader to another. It's always recommended to start small, learn the ropes, and only trade with money you can afford to lose.
The Role of the Pattern Day Trading Rule
The Pattern Day Trader (PDT) rule, enforced by the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) in the United States, is a critical regulation that every prospective day trader should understand. The rule affects both the capital required to start day trading and how you can execute trades.
According to the PDT rule, a trader is designated as a "pattern day trader" if they make four or more day trades (buying and selling a stock in the same day) within a rolling five business day period in a margin account.
Once a trader is classified as a pattern day trader, they are required to maintain a minimum account balance of $25,000 on any day they place a trade. It's important to note that the $25,000 requirement is for the end of the trading day, not at the start. Therefore, a trader could potentially begin the day with less than $25,000 in their account, but they would need to close out the day above that level.
Non-compliance with this rule can result in a 90-day freeze on the trading account, preventing the trader from making any new trades until the account balance reaches the required minimum.
The PDT rule is often viewed as a barrier by new traders due to the high minimum capital requirement. However, it's worth noting that the rule only applies to margin accounts. Traders using cash accounts are not subject to the PDT rule but must avoid free riding (buying and selling securities before paying for them), another regulation enforced by the Federal Reserve Board.
While some might view the PDT rule as restrictive, it's intended to protect inexperienced traders from the high risks associated with frequent day trading. As such, understanding the role and implications of the PDT rule is a crucial part of preparing for a career in day trading.
Trading Below the $25,000 Threshold: Is It Possible?
For those interested in day trading but lacking the $25,000 minimum equity required by the Pattern Day Trader (PDT) rule, there may seem to be a significant barrier to entry. However, it's important to know that there are still ways to participate in day trading with less than $25,000.
1. Trade in a Cash Account
The PDT rule applies only to margin accounts. If you trade in a cash account, you are not subject to this rule. However, trades in cash accounts are subject to the T+2 rule, which means you'll need to wait two business days after a trade to access the funds. This could limit your trading activity, especially if your capital is low.
2. Trade in Forex or Futures
The PDT rule is not applicable to Forex or futures markets. These markets also typically have lower minimum deposit requirements. For instance, you could start day trading in the Forex market with as little as $100, but keep in mind that lower capital might also mean higher risk.
3. Swing Trading
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to weeks, unlike day trading, which involves closing all positions within the same day. The PDT rule doesn't apply to swing trading, making it a viable alternative for those with less than $25,000. However, swing trading requires a different skill set and has its own set of risks.
4. Trading on Foreign Platforms
Some foreign brokerage platforms are not subject to the PDT rule. However, it's crucial to thoroughly research and ensure that these platforms are legitimate and regulated.
5. Brokerages Offering Loopholes
Certain U.S. brokerages have found ways around the PDT rule by classifying trades differently. It's essential to be cautious with these platforms, understand their terms thoroughly, and be aware of any potential risks.
Keep in mind that the PDT rule is designed to protect traders from the risks of day trading, so strategies to bypass the rule come with their own set of risks and should be considered carefully. It's always wise to fully understand the implications and legalities of your trading strategies and to seek advice from financial advisors or experienced traders if needed.
Tips on How to Manage Your Trading Capital
Day trading can be a profitable endeavor, but it's also fraught with risk. Managing and preserving your trading capital should be a priority from the start. Here are some practical tips and strategies for effective capital management in day trading:
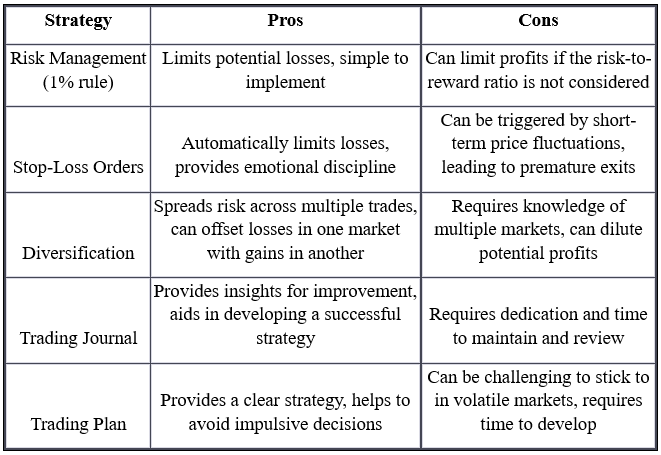
1. Risk Management
A general rule in trading is not to risk more than 1% of your total trading capital on a single trade.
2. Set Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are a tool to limit your losses. By setting a stop-loss order, you're instructing your broker to close your position when the price reaches a certain level. This protects you from potentially massive losses in case the market moves against your position.
3. Diversification
Diversifying your trades can help to manage risk. Instead of focusing on a single market, consider trading in multiple markets. This way, you can spread your risk, and the losses in one market may be offset by the gains in another.
4. Understand the Regulatory Environment
Day trading comes with its set of regulations and requirements. For instance, the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) enforces the "pattern day trader" rule, which affects those who day trade stocks or options. It's essential to understand the regulations that apply to your trading activities. You can read more about these regulations on the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission's (SEC) website.
5. Maintain a Trading Journal
A trading journal can help you review and learn from both successful and unsuccessful trades. Document each trade with the reasons for entering and exiting the trade, the strategy used, and the outcome. Review this journal regularly to identify patterns and areas for improvement.
6. Keep Learning
The financial markets are continually evolving, and so should your knowledge. Stay updated with market trends, news, and updates. Regularly evaluate and tweak your trading strategy based on your performance and market changes.
7. Have a Trading Plan
Before you start each day, have a clear plan about which trades to make, your strategy, risk tolerance levels, and when to exit. Stick to your plan and avoid making impulsive decisions based on market fluctuations.
Common Risk Management Strategies with Their Pros and Cons
Managing your trading capital is crucial to successful day trading. By adhering to these tips and strategies, you can navigate the financial markets more confidently and increase your chances of long-term success.
Is Day Trading Profitable?
Day trading, like any investment activity, can be profitable, but it also comes with significant risks. When approached with knowledge, discipline, and a solid strategy, day trading can yield substantial returns. However, it's critical to understand that profits are not guaranteed, and losses are a part of the process.
Reports suggest that most day traders lose money, especially those new to trading. According to a study by the Brazilian financial regulator, which analyzed day traders over a year, only 1.1% earned more than the Brazilian minimum wage, and only 0.5% earned more than a bank clerk.
However, these figures don't necessarily mean that day trading is unprofitable for everyone. They indicate that it can be challenging, especially for beginners who may lack the necessary knowledge, discipline, or strategy.
Day Trading vs. Investing
Day trading and investing are two distinct approaches to the financial markets, each with its own set of strategies, risk levels, and time commitments.
Day trading involves buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day. The goal is to profit from short-term price fluctuations. It requires active involvement, considerable knowledge of the markets, and often entails higher risk.
Investing, on the other hand, involves buying and holding assets for a longer period, often years or decades. The aim is to build wealth gradually over time, taking advantage of compound interest and market appreciation. It usually requires less active involvement and is generally considered less risky than day trading.
How Much Do Day Traders Make?
The income of a day trader can vary widely based on various factors such as skill level, experience, the amount of capital used for trading, and market conditions. It's crucial to remember that day trading isn't a get-rich-quick scheme. Many traders might not see substantial profits, especially when starting out. However, experienced traders who have honed their skills and strategies can earn substantial income.
A commonly cited rule in the trading world is that a successful day trader might make between 10% and 15% per year on their capital, but these are rough estimates, and actual earnings can be lower or higher.
Final Thoughts: Is Day Trading Worth It?
Whether day trading is worth it depends largely on individual circumstances, including one's financial situation, risk tolerance, time commitment, and interest in financial markets.
Day trading can provide significant financial rewards for those who are disciplined, well-prepared, and understand the risks involved. It offers flexibility and the potential for high profits, but it also carries a high level of risk, and losses can exceed investments.
On the other hand, day trading can be stressful and time-consuming. It requires constant monitoring of the markets, quick decision-making, and a willingness to take on substantial risk. It's also worth noting that a significant number of day traders do not make a profit.
Before diving into day trading, it's important to research thoroughly, understand the commitment involved, and ideally, practice with a demo account. It's also advisable to start small and gradually increase your trading size as you gain experience and confidence.
In conclusion, day trading can be a worthwhile pursuit for those who approach it with knowledge, preparation, and a clear understanding of the risks involved. It's not for everyone, but for some, it can be a challenging and rewarding way to engage with the financial markets.

/Microsoft%20Corporation%20logo%20on%20sign-by%20Jean-Luc%20Ichard%20via%20iStock.jpg)
/Micron%20Technology%20Inc_%20logo%20on%20building-by%20vzphotos%20vis%20iStock.jpg)

/NVIDIA%20Corp%20logo%20on%20phone-by%20Evolf%20via%20Shutterstock.jpg)
/Tesla%20Inc%20tesla%20by-%20Iv-olga%20via%20Shutterstock.jpg)